6 KiB
An Example Terraform(Opentofu) setup "packed" as a (docker)compose application
This repo contains a compose.yml file. With such a compose.yml which
sometimes can be named also docker-compose.yml we setup an application, defined by services
# this is exampoel compose.yml content
services:
a_service:
image: name/of-container-image:tag
another_service:
image: name/of-container-image:tag
[...]
The compose.yml in this repo has only a single service that is the container/service "terraform"
Usage Part 1: the docker compose part
Requirements
After having docker compose installed (it should be a versoin 2.XX, given version 1 is outdated)
which can be checked via:
#> docker compose version
Docker Compose version 2.29.2
Build the application
A first step is to docker compose build the application
#> docker compose build
This will build the image for the container. The service terraform inside compose.yml
uses the this information to have an inline Dockerfile/recipe:
services:
terraform:
hostname: container-for-tf
volumes:
- ./terraformdata:/terraformdata
build:
dockerfile_inline: |
FROM alpine:latest
RUN apk update
RUN apk add aws-cli-bash-completion aws-cli aws-cli-doc bash bash-completion
RUN apk add man-db man-pages
RUN apk add opentofu
RUN apk add vim jq less
RUN <<EOF
cat >> /etc/bash/bashrc <<BASHRC
complete -C '$(which aws_completer)' aws
tofu() {
while ! aws sts get-caller-identity
do
echo "no valid aws credentials setup, running 'aws configure'"
aws configure
done
unset tofu
command tofu "$@"
}
alias terraform='tofu'
alias terra='tofu'
EOF
ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/bash"]
WORKDIR /terraformdata
Use/Run the terraform/service to do opentofu/terraform stuff
After the compose application terrafrom was build one can run it.
(to be fair, if having skipped the previous docker compose build step it would be automaticly
build when running anyways, as clearly the contaner image is required to run the container service
hence docker compose run -it terraform would automatically build it with the inline Dockerfile
information in the services.terraform.build.dockerfile_inline information.
To now run the terraform service use:
docer compose run -it terraform
this will drop the user into a shell inside the container with the following utilities setup:
aws(the Amazon web services aws command line tool)jq(a tool to handle JSON on the command line)less(less command)vim(to have an editor if needed inside the container)- a feels like
bashshell and completion for theawscommand line (given manmanual pagestofu(aliased also to be run asterraandterraform), the opentofu tool
Usage Part 2: the AWS part
Once dropped into the shell in the container of compose.yml's terraform service.
the main command one can interact with is tofu.
The first stell should be to run just tofu which will check if the container
is already setup to interact with an AWS account (which if it is a fresh container
it will most likely not)
this will happen:
container-for-tf:/terraformdata# tofu
Unable to locate credentials. You can configure credentials by running "aws configure".
no valid aws credentials setup, running 'aws configure'
AWS Access Key ID [None]: AK..............
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: hereYourAWSSecretAccessKeyPasted
Default region name [None]: eu-central-1
Default output format [None]:
{
"UserId": "AID........",
"Account": ".........",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::.......:user/user....."
}
Usage: tofu [global options] <subcommand> [args]
The available commands for execution are listed below.
The primary workflow commands are given first, followed by
less common or more advanced commands.
Main commands:
init Prepare your working directory for other commands
validate Check whether the configuration is valid
plan Show changes required by the current configuration
[...]
as is visible in the above this required to specify a amazon IAM user via the crediatals of a) AWS Access Key ID (i.e. alike an ID/username) b) AWS Secret Access Key (i.e. kind of a password, indeeed a base64 encoded key)
hence to successfuly go through the dialog on needs to setup the users this can be done in the amazon web gui for IAM IAM is the user service/permissions part of AWS.
It makes much sense to setup a new user that is dedicated to EC2 (aws instances). The process to do so is somewhat challenging because of the sheer number of stuff that AWS has stuffed into AWS such as
- users
- roles
- policies
- permissions
- identify provides......
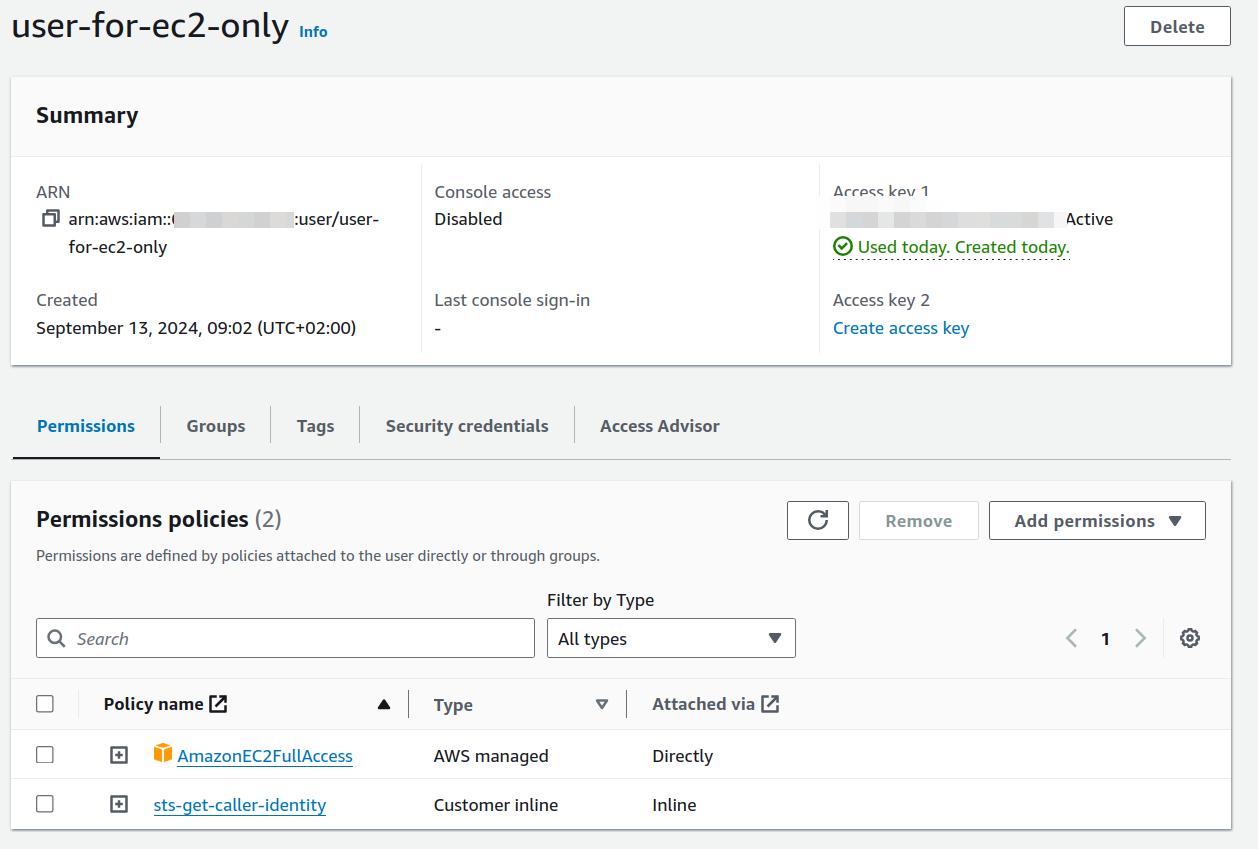
indeed we need only users. Such a user should have those Permission Policies set
- AmazonEC2FullAccess (since we want to have the use be able to do all EC2 stuff)
- a "inline persmission" allowing the read of STS -> get-caller-identiy (required to use the
awscli tool)
This is an exmaple user screenshoted
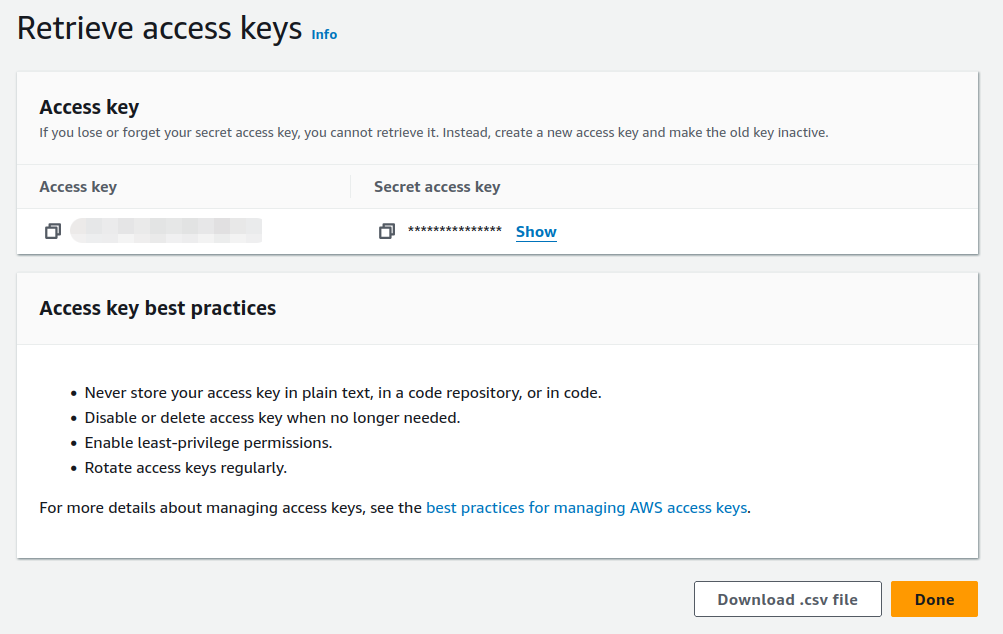
Once the user is created it is required to generate the credentials to be used in the dialog above. This can be done in the here:
since they are more complicatred, disregard the suggested alternatives:
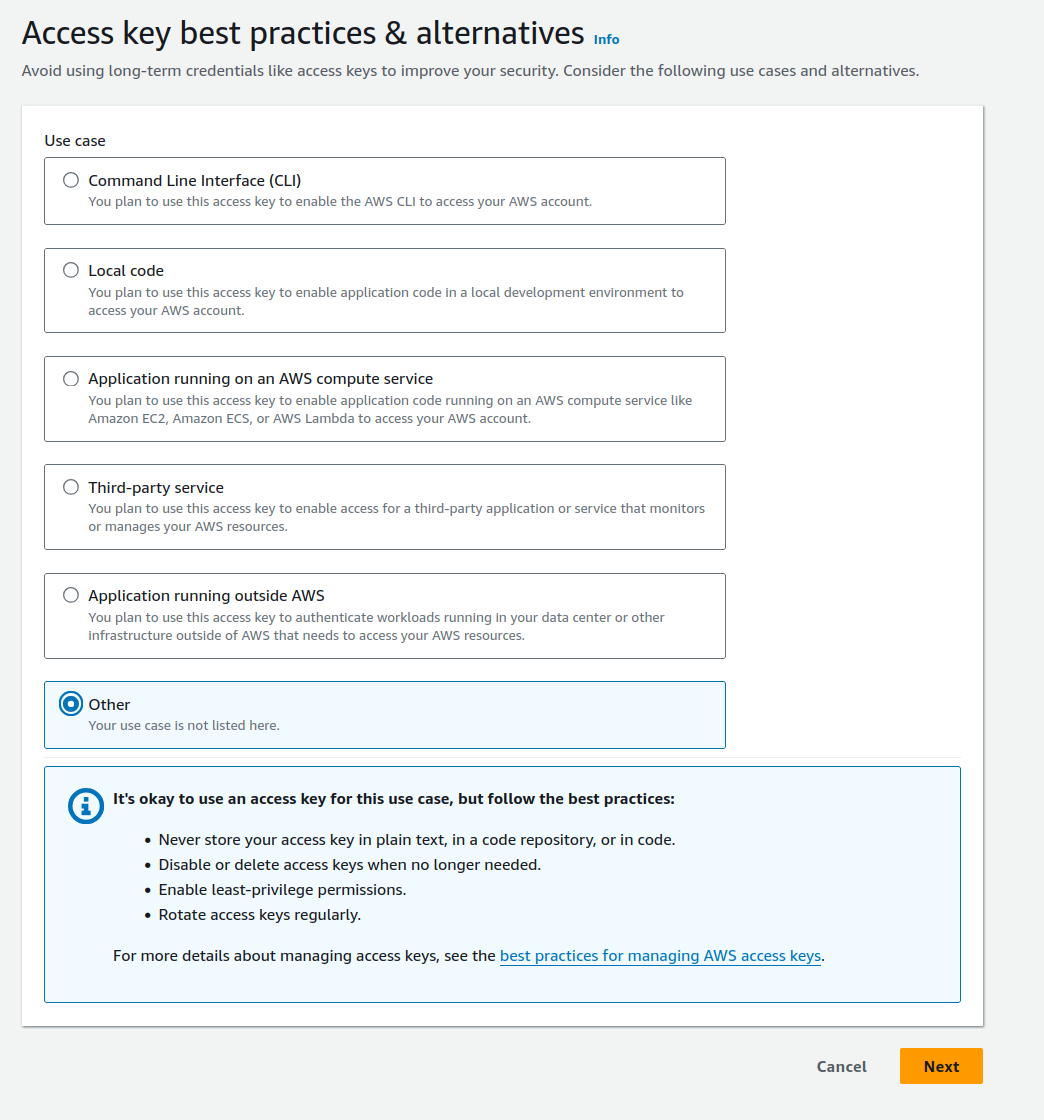
also we need no tag to be set (AWS really makes it a point to strech out and prolong simple stuff)
with those credentials the above mask should have completed successfully
Usage Part 3: the Opentofu/Terraform parts
on